Obsidian: [[04-01-01-U_FluidNinja Fluid Ninja]] [[16-01-01-VFX VFX]]
Optimisation : -Effect Types - like texture groups backbone of optimisation and scalability
https://youtu.be/vOSXl7-2vd0 Interactive VFX systems https://80.lv/articles/drawing-locations-to-a-render-target-in-unreal-engine-5-1/ Grid 2D to Render Target YT UE Optimising Niagara
Interaction spaces
- Triangles - u must point to specific mesh in query
- Phys Volumetric -
- Scene Depth - 2d buffer, don’t penetrate behind first depth
- Distance Fields -
Paradigm
- Modules - graph paradigm
- Emitters - stack paradigm
- Systems - stack and Sequencer timeline
Calculation stages
System
- Module usage flags
System Spawn Script- on system spawnSystem Update Script-
Emitter
Do what system (optimal to set for multiple emitters) do or define.
- Module usage flags
Emitter Spawn Script- once on spawnEmitter Update Script- Tick
Particle
- Module usage flags
Particle Spawn Script- on spawnParticle Update Script- every frameParticle Event Script- In response to eventParticle Simulation Stage Script-
Spawn
Update
Scripts
Dynamic Input scripts
Dynamic Input scripts by Usage flag:
Module
Use as module in particle emitter.
Read/Writes parameters will appear in module.
Can be used with: particle , emitter, system scripts
IN: Map OUT: Module
Dynamic Input
Use as expression in parameter value. Almost the same as creating modules, but can be selected and dropped into the stack without actually creating new modules. (extensibility for inheritance. Instead of acting on a parameter map, dynamic inputs act).
Can be used with: particle , emitter, system scripts
IN: Map OUT: Module
Function
Functions to use inside module.
IN: Input OUT: Output
Attributes
Name Space
| Name Space | R | W | Define | Share within |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PARTICLES. | Particle | Particle | Persisted f2f | Loaded as payload. Per-particle (@point) |
| INPUT. | Y | N | Module input. Use inside of module for promoted Parameters | |
| Module | Module | Module | Module | expose a module input to the System and Emitter Editor |
| LOCAL. | Module | Module | Not persist f2f | Transient values. Truly local for function ! Transient values. |
| EMITTER. | Emitter, Particle | Emitter | Persisted f2f | Emitter instance / color ect… |
| SYSTEM. | Y | System | Persisted f2f | System |
| ENGINE. | Y | N | Runtime for Niagara itself | Fundamental Attribs from unreal |
| USER. | Y | N | ||
| OUTPUT. | N (An output in Particle Spawn cannot be accessed in Particle Update) | Y | Not persist f2f | pay for calculate but not for adding it to emitter (parameter writes) useful helpers included in the modules which are not yet written to the particle payload, but are available for use. |
| TRANSIENT. | from any module | from any module | Not persist f2f | Local only to a given stack context (like Particle Update) |
Name space modifiers:
| Name Space | R |
|---|---|
| .MODULE. | insert module name as namespace so if u have x modules u have x different params |
| .INITIAL. | initial value of attribute (from eg in particle spawn) |
Particle attributes vs Transient outputs:
- Transient - Not persist f2f and between stages, not written to the payload, which means they don’t cross stack boundaries and are recalculated from scratch every frame
- Particles - Persisted f2f (memory and performance cost)
Orientation
Mesh
Set Orientation
Inexpensive constant rotation rate. (rotational drag, an option on the drag module) has no effect.
set: Particles.MeshOrientation
Update Mesh Orientation Module -
Orient Mesh To Vector Module - Can be after solve forcces
Rotational Force
Paradigm which factors mesh scale, mass, density, and drag into the model. larger meshes have a tendency to resist rotation due to their mass, and rotational drag can be used to control the acceleration/deceleration. Transient.PhysicsRotationalForce
"Mesh Rotation Force" Module in Particle Update -
Solve Rotational Forces and Velocity Solver -
Drag
Need “Initial Model Dimensions” and mass > “Calculate Size by Mass”
Rotational Velocity / Drag
Rotational Forces accumulate into a Particles.RotationalVelocity variable and persist from frame to frame. Here we give the particles an initial “kick”, by applying a Rotational Force and then applying those forces to the Rotational Velocity. We use this method as it factors mass into the initial rotational velocity.
This then gets solved by the solver in update, and rotational drag eventually slows the particles down.
If you want the initial “kick” to not factor in mass, you can use an “Add Rotational Velocity Module” to directy set a rotation speed.
Mesh Rotation Force Module in Particle Spawn -
Apply Initial Forces Module
Inheret Velocity - In Update, magnify velocity of root (have limit)
Static Mesh Velocity with sample static mesh - will have velo of mesh Normal
Vortex velocity
Sprite
Orient Mesh along vector
Alignment
` Particles.SpriteFaceing` - is the vector variable which controls which direction a particle faces
SpriteAlignment
SpriteRotation
SpriteUVScale
SpriteSubimageIndex
(in particles.)
Velocity
[Add Velocity] / [Add Velocity from point] / [Add Velocity in cone]- in particle spawn (ever frame if in update)
Coordinates & Space
Simulation, World, Local
Mesh Tri Coordinates > Bary Coords
Physics
Solve Forces and velocity
Write to intrinsic properties
Choose whether or not to write to intrinsic properties
ENGINE.DelatTime
ENGINE.OWNER.Position
Emitter Local Space
Masss Position Previous.Position, Velocity, Previous.Velocity,
TRANSIENT.PhysicsDeltaTime
TRANSIENT.PhysicsDrag
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce
- (time) Fractional updates based on collision equations
- (Init copy:)
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce>LOCAL.PhysicsForce,OUTPUT.MODULE.IncomingPhysicsForcePARTICLE.Velocity>OUTPUT.MODULE.VelocityPARTICLE.Mass>LOCAL/PARTICLE.Position>OUTPUT.MODULE.Position- copy to >
PARTICLES.PRESOLVE - (Apply mass to phys)
- (1/
LOCAL.Mass) *LOCAL.PhysicsForce>LOCAL.PhysicsForce
- (1/
- (Apply forces to velo) (copy drag irrespective of Mass)
OUTPUT.MODULE.Velocity*LOCAL.DelatTime*LOCAL.PhysicsForce>OUTPUT.MODULE.VelocityTRANSIENT.PhysicsDrag>OUTPUT.MODULE.IncomingPhys
- limit velko and acc
- (Apply velo to pos)
OUTPUT.MODULE.Velocity*LOCAL.DelatTime*OUTPUT.MODULE.Position>OUTPUT.MODULE.Position- [T] copy
OUTPUT.MODULE.Position/ >PARTICLE.Position/Velocity>Velocity- If Forces/Drag have been converted to Velocity, zero out
- [T] 0 >
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce/PhysicsDrag
PARTICLE.Position
PARTICLE.Velocity
Presolve pos, velo
Presolve physic forces
TRANSIENT.PhysicsDrag
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce
Point Attraction Force
EMITTER.LocalSpace
PARTICLE.Position
PARTICLE.Velocity
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce
…
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce
Point Force
EMITTER.LocalSpace
PARTICLE.Position
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce
…
OUTPUT.POINTFORCE.Withinrange
OUTPUT.POINTFORCE.NormalizedFallof
OUTPUT.POINTFORCE.NormalizedDistance
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce
Limit Force
Drag
Acceleration, Avoid, Gravity, Line Attraction, Linear, Mesh Rot, Spring, Vector Noise, Vortex, Wind
Houdini Combine Forces
.
- Copy
PARTICLES.NiagaraForce>TRANSIENT.NiagaraForce- 0 >
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce - Lerp
- Lerp
PARTICLES.Velocityor (PARTICLES.HOUDINI.VelocityorPARTICLES.HOUDINI.GoalPosition) >PARTICLES.Velocity - Apply
PARTICLES.NiagaraForce>TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce
PARTICLES.NiagaraForcesMultiplayer
PARTICLES.Velocity
TRANSIENT.PhysicsForce
Render
HLSL
Micro Expressions
/* Custom HLSL! */sin(Emitter.Age *0.3) /2 +0.5- 0-1 time x 0.3cross(Particles.RandomVector, float3(0,8,0))- crossrand(1.5f) + 2.2f- randomlength(Particles.Position - Emitter.InitialPosition)- lengthsaturate()- fast clamp 0-1frac(Emitter.Age *0.3)- 0-1 loop in time x 0.3float3(0.0f, 0.0f, Emitter.ZOffset) *0.2f)- Add ZParticles.Position + float3(0, 0, (sin(Engine.Time) * 0.3f ))- Add Z sin to actual pos
.
float3(Particles.UV,0)- make vector from uvs(Particles.Position-Particles.PreviousPosition)/Engine.DeltaTime- render velocity
.
Emitter.InitialPosition + Particles.RandomVectorParticles.NormalizedAgeParticles.Position - Emitter.InitialPosition
.
(1.0f-(abs((Particles.RibbonLinkOrder)-0.5f)*2.0f))*50.0f- Ribbon radious
Conditioning
Particles.NormalizedAge<0.3 ? float4(1,0.1,0.1,1):Particles.NormalizedAge<0.5 ? float4(1,1,1,1):float4(1,1,1,1)
Particles.Position.z > Emitter.InitialPosition.z - Emitter.ZOffset
? Particles.Position
: float3(Particles.Position.x, Particles.Position.y, Emitter.InitialPosition.z -Emitter.ZOffset)
Map Attributes
Time:
Engine.DeltaTime/InverseDeltaTime/Owner.TimeSinceRendered/RealTimeEmitter.AgeSystem.Age/TickCountTime-Particles.Age-Particles.NormalizedAge- 0-1Particles.Lifetime-Module.DeltaTimeModule.LifeTimeModule.LoopParticlesLifetime
Translation
Particles.Position- @PParticles.Scale- @pscale (mesh)Particles.SpriteSize- @pscale (sprite)Particles.RibbonWidth- Ribbon widthParticles.Owner.Position/Rotation/Scale- Owner Transform
Physics
Particles.MassParticles.Velocity- @vParticle.PreviousVelocity- @vEngine.Owner.VelocityPhysics.ForcePhysics.DeltaTime
Render
Particles.MaterialRandom- FloatParticles.Color- Linear ColorParticles.DynamicMaterialParameter- Vector 4Particles.CameraOffsetParticles.UVScale
Tips
- Niagara 16 params can send to material
- U can access only depth buffer can read
- Use: Inheritance. You can always reparent
Interfaces
The Kill Particles module at spawn - acts as a form of “Rejection Sampling”. We sample the texture and then kill the newly spawned particles on their first frame if the sampled texture alpha equals 0.
Because Interpolated Spawn is unchecked in the emitter properties, newly spawned particles do not run both their spawn and update scripts on the frame they were born, making this technique quite inexpensive.
Particles.VisibilityTag - Render Visibility - can change renderer dynamicly
Ribbons
`NiagaraRibbonRendererProperties` module.
##### Ribbon Render
Ribbon - `Particles.RibbonFaceing`, `RibbonLinkOrder`, `RibbonTwist`
##### more ribbons
`SetRibbonIDByExecOrder` - get the particles execution index, make a Niagara ID and assign the execution index to the ID index, and then set `Particles.RibbonID` in the Map with our new ID.
-
`Particles.RibbonLinkOrder` is the variable which determines how particles of a given `RibbonID` link up with each other.
The Spawn Beam module establishes the order based on the new particles as they are spawned in a burst, and assigns a new unique `RibbonID` to each new set of particles so they stay as separate beams instead of one large interconnected ribbon between all particles in the emitter.
From there, normal particle simulation takes over, and because the ribbon ID and link order are not changing from frame to frame, the beams stay stable.
## Events
push
Will be 2.0! cause of fixed payloads (could be arbitrary )
Location Event
CPU
Leader emitter
Particle update
Generate Location Event
Follower emitter
Event Handler
Event Handler Properties - Event Handler
Recive Locaation Event - Event Handler
Which runs after the event is received. This needs to include a “Receive X Event” Module to handle the event, and then other modules can be placed inside to have additional effect on the particles which receive events, for example an additional location module to provide an additional offset from the received event position.
Attribute Reader
GPU
Spawn Particles From Other Emitter and Sample Particles From Other Emitter modules which utilize the Particle Attribute Reader. Listen to other emitter (events not push, but pull directly) - bats, flock, swarming bugs, Flight Orientation
Get by ID - niagara unique particle qttribute
Get Vector by index – get attribute (like Color) by Index (order particle responce)
Get Spawned ID at Index > Get Vector by ID
- can use it on yourself every particle can ask of neighbour pos (phys line)
- can integrate with otherforces (like cable component in niagara) and
newParticleAtributeReader
Constraints
Vector Fields
.fga
add an Acceleration Force module under our Sample Vector Field, and then bind the value SampleVectorField.SampledVector to the Acceleration value
VectorFieldSize
http://andy.moonbase.net/archives/1499
Distance Field
Sample Distance Field
Collision
CPU
Expensive, should be used sparingly.
- can optionally generate events using the “Generate Event” (Receive collision event)
Collision- Ray Traced
Generate Collision Event
GPU
Direction and D-buffer sampling
- can sample the scene depth, or the global distance field.
Collision- GPU Distance field / GPU Depth Buffer. Can be used at the end of particle update (before solvere) or special collision module.
Collision module
-
Place a Solve Forces and Velocity module at the end of particle update. Ensure that the “Write to Presolve Parameters” checkbox is set to true.
-
Place a Collision module in a final simulation stage.
The simulation stage should operate on “particles” and perform 1 iteration.
- A second “Solve Forces and Velocity” module should be placed immediately after the collision module. That module’s “Write to Intrinsic Properties” Bool should be driven by [Transient]CollisionValid.
Neighbor Grid 2D GPU
Sampling image - value to sample the texture as if it were a UV.
Spawn Particles In Grid - Emiter up
Grid Location
Sample Texture
Neighbor Grid 3D
special position cash when a lot of particle need global comunication
PBD
Mesh Reproduction Static
Set position from static mesh
Set UV by Dynamic material
Mesh Reproduction Skeletal
initialize mesh reproduction
Particle Update
update mesh reproduction
Material
- add Niagara mesh reproduce uv’s
Houdini Point Clouds
Houdini
Niagara ROP
Export pointcloud as: .hjson, .hbjson - bin quicker
i@idper particle same for one particlef@timeof pop-up / arrival time // just normalize time before export! check length from a to b and set time@typegroup@lifeLife set for first pointi@dead = 1NID- niagara id attrib CREATED BY SAMPLE MODULES
noForce?
hardcoded attributes -
Unreal
Emitter Spawn
InitHoudiniPointCache - Initialize
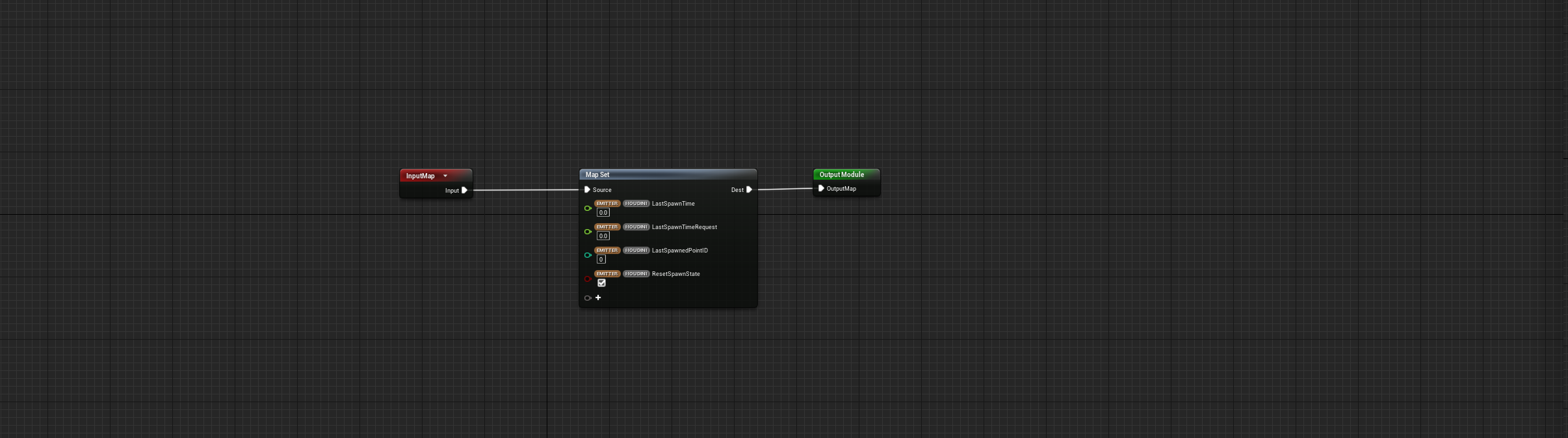
.
W:
emitter.Houdini.LastSpawnTime - 0.0
emitter.Houdini.LastSpawnTimeRequest - 0.0
emitter.Houdini.LastSpawnedPointID - 0
emitter.Houdini.RestSpawnState - [V]
Emitter Update
SpawnParticleFromHoudiniPointCache - Spawn only
GetPointIDTospawnAtTime- create spawn data: deltaTime, InterpStart, Delat, Count
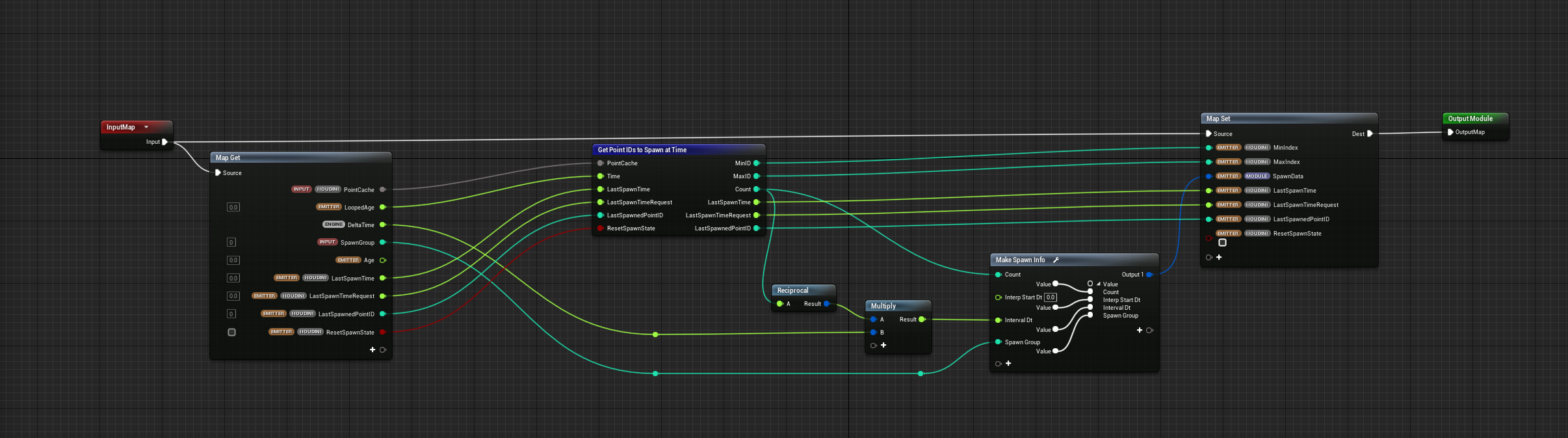
.
R:
engine.DeltaTime
emitter.LoopedAge
R/W:
emitter.Houdini.LastSpawnTime - 0.0
emitter.Houdini.LastSpawnTimeRequest - 0.0
emitter.Houdini.LastSpawnedPointID - 0
emitter.Houdini.RestSpawnState - [V]
W:
emitter.Houdini.MaxIndex
emitter.Houdini.MinIndex
emitter.Houdini.ASpawnParticlesFromHoudiniPoinCache.SpawnData
Particle Spawn
SampleSpawnHoudiniPointCache - sample data not set! (similar to sample niagara mofules )
- Creat
NID- Particles.Houdini.NID: This is not the same value as the original ID attribute. This is the persistent Niagara ID that should be used for attribute lookups. GetPoint...AtTime-Transform...- Local to sim for: P, N, v
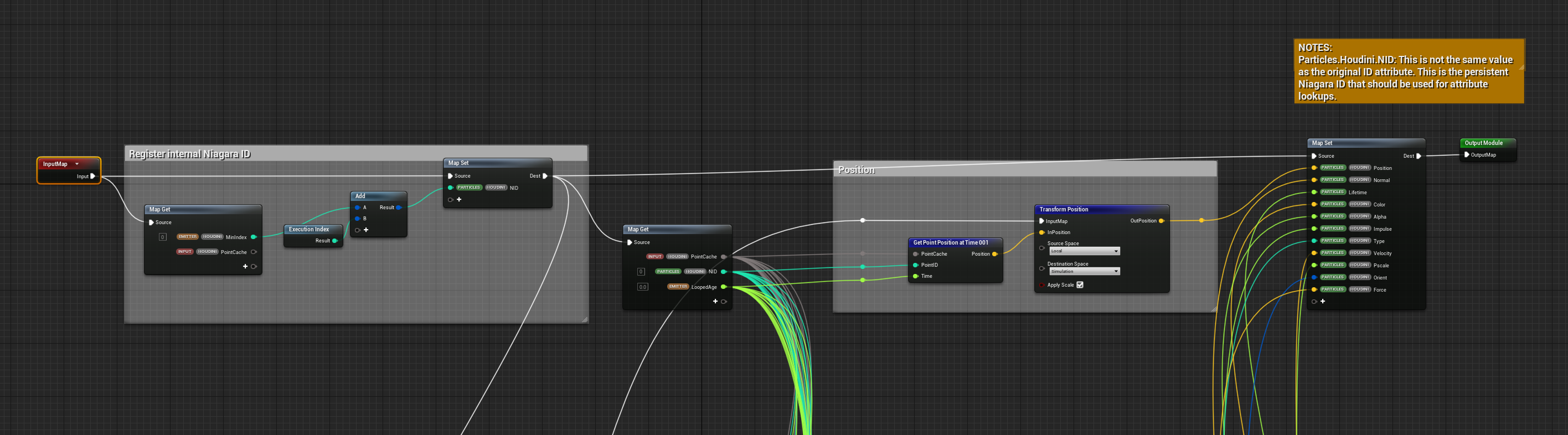 .
.
R:
engine.Owner.SystemLocalToWorld
engine.Owner.SystemLocalToWorldNoScale
engine.Owner.SystemWorldToLocal
engine.Owner.SystemWorldToLocalNoScale
emitter.Houdini.MinIndex // optimistaion > NID
emitter.LocalSpace
emitter.LoopedAge
R/W:
particles.Houdini.NID
W:
particles.Lifetime
particles.Houdini.Alpha // f@Alpha
particles.Houdini.Color // v@Cd
particles.Houdini.Impulse // @impulse
particles.Houdini.Normal // v@N
particles.Houdini.Orient // 4@orient
particles.Houdini.Position // v@P
particles.Houdini.Pscale // f@pscale
particles.Houdini.Type // type
particles.Houdini.Velocity // v@v
Particle Update
SampleHoudiniPointCachce
GetSampleIndexesForPointAtTime- get sample index and BlendAlphaGet...- and LERPNF Transform Vector(Local to Sim) +NF Initial Particle Postition(engine.Owner.Position)
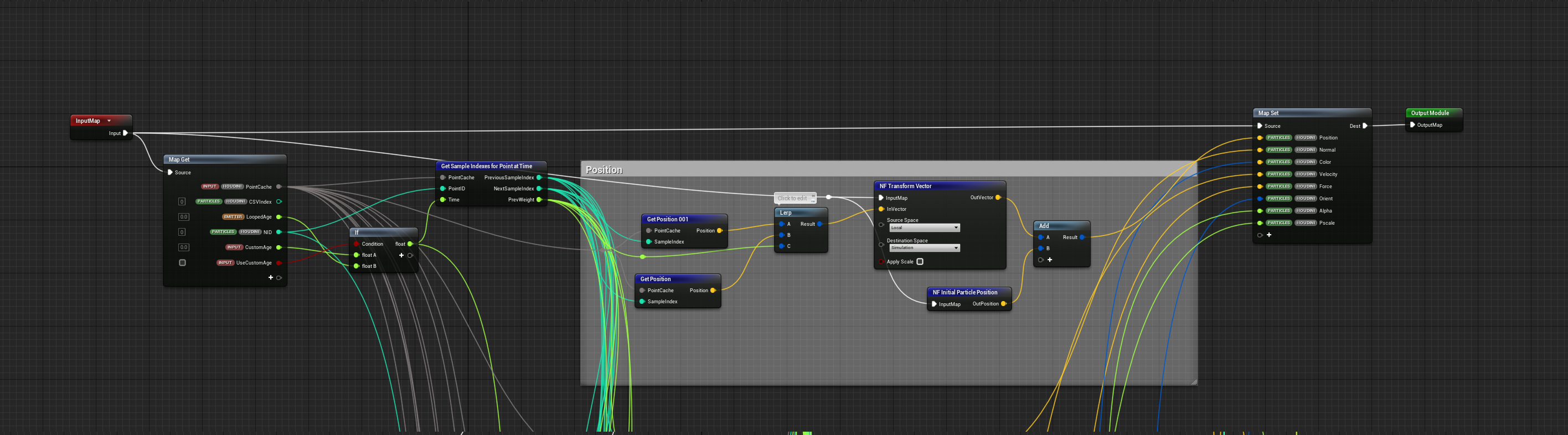 .
.
R:
engine.Owner.SystemLocalToWorld
engine.Owner.SystemLocalToWorldNoScale
engine.Owner.SystemWorldToLocal
engine.Owner.SystemWorldToLocalNoScale
engine.Owner.Position
emitter.LocalSpace
emitter.LoopedAge
particles.Houdini.NID
particles.Houdini.CSVIndex
W:
particles.Houdini.Color // v@Cd
particles.Houdini.Force //
particles.Houdini.Normal // v@N
particles.Houdini.Orient // 4@orient
particles.Houdini.Position // v@P
particles.Houdini.Velocity // v@v
- set
particle.position>particle.Houdini.position- drag and assign houdini particle positiopn - set
Color>vector and float>Particles.Houdini.Color - set
KillParticles> (see custom script)
CombineForce
Custom attributes script
New niagara module script: custom attributes:
Map get > [Get Vector Attribute By Name] > set Input.HoudiniCache
(in parameters)
[EmiterAttribute] > Input.HoudiniCache >
[ParticleAttrbute] > Particles.int32 (right namespace add modify to: Particles.Houdini.NID )
[EmitertAttribute] > Emiter.Age
Houdini trigger
R:
`engine.DeltaTime` -
`emmiter.TimerActive`
R/W:
`emitter.DistanceToPlayer`
`emmiter.HoudiniCacheTime`
`emmiter.MoveToStartTime`
`emmiter.NiagaraForcesMultiplayer`
`emmiter.T3.Execute`
`emmiter.T4.Execute`
`emmiter.T5.TriggeredOnce`
`emmiter.TimeToRest`
`emmiter.TriggeredOnce`
W:
`emmiter.T1.Execute`
`emmiter.T2.Execute`
`emmiter.T5.Execute`
`emmiter.TriggerSomething`
Sources
Houdini niagara - ue plugin
Houdini Extras - ue plugin
UNREAL FOR ALL CREATORS zobacz -
SideFx
2020 04 SideFx Niagara(frompluginContent) / Demo2020 (water Paul)
2020 11 SideFx - 2020 11 SideFx YT - to samo co wyzej
Unreal
2018 11
2020 04 Inside Unreal - Houdini workflows / paul / crowd / chains
2020 05 Unreal - Building advanced effects in Niagara Unreal Engine character
2020 05 Unreal talk Wyeth
2020 08 Unreal Fest Online 2020 dek kart
2020 11 Advanced Niagara Effects Inside Unreal - popcorn
RTVFX
Particle Location Module Mini Tutorial - Near Surface Location Mini Tutorial - Using splines for GPU particles - Spline Location Mini Tutorial - Rope Physics Mini Tutoria - Near Surface Location Mini Tutorial - Ribbon Trail Mini Tutorial - UE4 Niagara Audio Visualization (passing data from BP to Niagara) - RTVFX pack
tuts
- Fluid ninja 80 / Fluid ninja pdf / Fluid ninja YT
- YT BTM series tutki
- creative unreal table
- YT BTM series tutki
Camera Interface
on gpu more control. on cpu only on simulate will work
input.newCameraquery > GetCameraProperties - gpu/cpu properties
newCameraquerry > PropertiesGpu
get Field Of View
Get View Space Transform GPU - tarnsforms
View Properties GPU
(in input)
Audio Interface
AudioOsciloscope - Direct access to waveform. high/low freq 1:1 waveform mapping
AudioSpectrum - Buckets fft
Play Audio module
Occlusion
GPU
Occlusion of point in time can do for point ()
NewOcclusionQuery -
Occlusion Factor With Circle / Rectangle GPU - compare to depth bufer
``` Future:
- ray matching particle sprites/ meshes
- accum light in particle
- vdb