Pxlink: Obsidian: [[01-01-01-Circuit | Circuit]] [[01-01-01-Keystep | Keystep]] [[01-01-01-Reface | Reface]] [[03-01-01-Synthesizers | Synthesizers]] [[01-01-01-Ableton | Ableton]]
isolated VOCAL SAMPLES: https://www.reddit.com/r/nextfuckinglevel/comments/167mlrj/stevie_nicks_and_fleetwood_macs_satisfying/
All music genres 1 , All music genres 2 , Music Basics, YT Music Theory
https://sound-effects.bbcrewind.co.uk/
Sounds
Spectral signature
Any sound can be described in terms of its duration; pitch; dynamic; and timbre.
Dynamic
Amplitude
Loudness in Decibels
- Peak volume - highest, not usefull
- RMS volume - Root Mean Square (average over time) RMS Higher when there is no quiet parts.
- LUFS - RMS that take only ear related frequencies.
Dynamic Range
Ratio of the amplitude of the loudest possible undistorted signal to the noise floor. Dynamic range differ by genre. limiter / comresor /
Pitch
Highness or lowness.
| Range of human hearing | Wavelengths | |
|---|---|---|
| Air / Brightness | 10-15 kHz (Short Wave) | high pitch |
| Hi-Hats / Cymbals / Shimmer | 8-10 kHz | |
| Sibilance | 6-7 kHz | |
| Presence | 5 kHz | |
| Vocals | 2-4 kHz | |
| Snare | 1kHz (1000Hz) | |
| Mud | 300 Hz | |
| Kick | 100 Hz | |
| Bass | 60-80 Hz | |
| Sub Bass | 40Hz (long wave) | low pitch |
Length
| 𝅝 | 1 |
| 𝅗𝅥 | 1/2 |
| 𝅘𝅥 | 1/4 |
| 𝅘𝅥𝅮 | 1/8 |
Effects
Drive
Tremolo Wah Chorus Phaser Digital Delay Analog Delay Reverb
Rhythm
Events in time. Popular in Entrainment and ancestor roots.
- https://youtu.be/GHb_fLWKB_4
- interval - distance
Tempo (Agogika)
40 - 240 BPM
Hz - number of cycle per second
(jeśli zmieniasz tempo to automatycznie czas trwania nuty będzie się zmienał)
http://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-bpmtempotime.htm
Dub: 60-90 bpm Hip-hop: 60-100 bpm House: 115-130 bpm Techno/trance: 120-140 bpm Dubstep: 135-145 bpm Drum and bass: 160-180 bpm
Reggae 60-90 Down-tempo 70-100 Chill-out 90-120 Hip-hop 85-115 Jazz and Funk 120-125 Pop 100-130 R&B 60-80 Rock 110-140 Metal 100-160
House 118-135 Deep House 120-125 Tech House 120-135 Electro House 125-130 Progressive House 125-130 Trance 130-145 UK Garage 130-135 Dubstep +/- 140 Trap +/- 140 Techno 120-160 Hardstyle 150 – 160 Jungle 155-180 Drum and Bass 165-185
Waltz 84 – 90 Foxtrot 112 – 120 Charleston 200 – 290 Tango 62 – 66 Cha Cha Cha 120 – 128 Rumba 100 – 108 Samba 96 – 104 Salsa 180 – 300 Jive 168 – 184 Paso Doble 120 – 124
Beat
Rownomiernie rozmieszczenie dzieli muzyke na rowne czesci Sync brain with repeating https://youtu.be/2UphAzryVpY
Time signature:
- Top number: How many beats per mesure (ile wartosc i takcie )
-
Bottom: Which note duration recive the count (jakie wartosci w takcie) get the beat
- Top number: do ilu liczymy
- Bottom: mniej wazna (4 lub 8 zazwyczaj)
Drumkit
Percusive sounds: (tune in key cause of tail. (sometimes not audiable key)
Tonal sounds: Tail of Kick sometimes is tonal (Tail) how many Hz (55Hz > A (like orginal 808)) so sometimes u may tunew ti but not much. tune to interval that is plesent for your scale (not always root)
| Drums | Usage | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DK - Kick / Bass Drum | Wave high to low. Elements : 1) Transient hi 1000 Hz (high is clicky) 2) Thump (mid freq 120Hz) hit in chest 3) Tail (sustain) low stable 55 Hz (under 50 is hard to reproduce) | root & 5th: stable feel ). Balance low and highs, | lowest pitched Regular but often-varied foundation to the rhythm. |
| DB - 808 | Longer used as bass line | ||
| DT - Tom | Drums without snares (hi low mid LT MT HT ) (Octoban - Tube Toms) | (syncapation - highligh on one of weak beat). | Complete grove in down end. |
| SD - Snare | Heart of the drum kit, - snare should slap | Strong regular accents, (2 i 4 snare - backbeat ) | |
| RS - Rim Shot | Sharper, brighter and more cutting than a standard accent. produces large amounts of overtones | Snare + loud, woody accent. | |
| Cymbals | |||
| CH - Closed Hi-hat | Close after time, partially or fully (on edge/ on center ) | on upbeat or 16th note rolling (every note), …. make velocity gradient or lfo to get pumping feeling | (emphesise upbeat) |
| OH - Open Hi-hat | Lots of expressions. can close hat but dont play OH i CL at same time. Close will cut off open hat it give energetic direction, dancy. | ||
| RC - Ride | (swish cymbal, flat ride is a ride cymbal without a bell) (on top. high splashy energy) | every 8th note on upbeat | Steady rhythmic pattern |
| CY - Crash | (china- markers within the kit a distinct type of crash cymbals designed to produce a bright, crisp, and explosive tone. | Strongest accent | |
| CY - Splash | Smallest accent | ||
| Percusion | |||
| SH - Shakers | Create groove | ||
| CP - Claps / Tick / Klick / Wooden bell, Chime tree | |||
| CB - Cow bell / Gong / Sizzle- z wrkoczykami |
Bass: -Phasing - playing to close Htz. (beating) it can suck out punch from kick drum.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Downbeats | Strongest | X | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| Upbeats | Weaker | x | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| backbeat ?? | |||||||||||||||||
| weak 16 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
Patterns
- https://hiphoptranscriptions.com/
- https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/19_3BxUMy3uy1Gb0V8Wc-TcG7q16Amfn6e8QVw4-HuD0/edit#gid=0
- https://youtu.be/tm2BgO1VaRY
- https://archive.org/details/260DrumMachinePatterns/page/n5/mode/2up
Techniques
Swing
Breaks
Energy manipulation
- take kick,
- epic buildup Fx
- give back lows
Endegy turn off
- go to calm way low energy moment
- rise not kick yet (crushendo)
- silence
- dark
Rumble
1 channel kick
2 channel kidck + rumble
rumble =
- smear (reverb or sth),
- convert to mono
- low pass, keep only low like earthquake 200hz
- duck side chain to empty kick (pump it grove) then: -saturate (heavy saturation is like breaked mic)
Flames
- 2 uderzenie z przesunieciem
Flanging /ˈflændʒɪŋ/ is an audio effect produced by mixing two identical signals together, one signal delayed by a small and gradually changing period, usually smaller than 20 milliseconds. . bit crush —
Melody
Everything u can sing
Notes
| interval ratios | interval ratios | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Unison | P1 | 1 | 1:1 | root |
| 1 | Minor Second | m2 | 1.06(6) | 16:15 | Most dissonant |
| 2 | Major Second | M2 | 1.125 | 9:8 | More dissonant |
| 3 | Minor Third | m3 | 1.2 | 6:5 | Dissonant |
| 4 | Major Third | M3 | 1.25 | 5:4 | Usefull Consonant |
| 5 | Perfect Four | P4 | 1.33 | 4:3 | Usefull More Consonant |
| 6 | Tritone | 1.4 | 7:5 | unstable, harmonic disonante (tension) | |
| 7 | Perfect Fifth | P5 | 1.5 | 3:2 | Useful More Consonant |
| 8 | Minor Sixth | m6 | 1.66 | 5:3 | Usefull Consonant |
| 9 | Major Sixth | M6 | 1.6 | 8:5 | Dissonant |
| 10 | Minor Seventh | m7 | 1.8 | 9:5 | More dissonant |
| 11 | Major Seventh | M7 | 1.875 | 15:8 | Most dissonant |
| 12 | Perfect Octave | P8 | 2 | 2:1 | ——————– |
| 13 | Minor Ninth | m9 | 32:15 | ||
| 14 | Major Ninth | M9 | 9:4 | ||
| 15 | Minor Tenth | m10 | 12:5 | ||
| 16 | Major Tenth | M10 | 5:2 |
Tonic
Root / Key / Tonic Note - first scale degree. It is the tonal center and is the most stable note. Most often music ends on tonic because it’s a good resting point and gives a sense of finality. This is possibly the easiest note in a scale to remember because it is one of two notes most often called by it’s scale name.
Supertonic
2nd note in scale.
Scales
Set of notes ordered by pitch. half step = semitone = +1(of12)
- use only W and WH
- H cannot neighbors
- W & WH cannot neighbors
Accidentals
♯ Sharp - Rise by Half Note
♭ Flat - Lower a note by one Half Tone
♮ Natural - Cancels previous sharp/flat
Major more happy
Minor sad Major & Minor are relative. minor start on 6th note of Major (C Major = A minor )
Pentastonic - There are both Pentatonic Major and Minor – the Minor is slightly more often used
Whole tone - dont have 4th and 5th (triads - only augumented) nice donbt have ‘tritones and can sound nicer’
| Major root | Major | Minor root | Minor Natural | Minor Harmonic | Minor Melodic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 | 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 | 2 2 1 2 1 3 1 | 2 1 2 2 1 3 1 | ||
| C |  |
A | 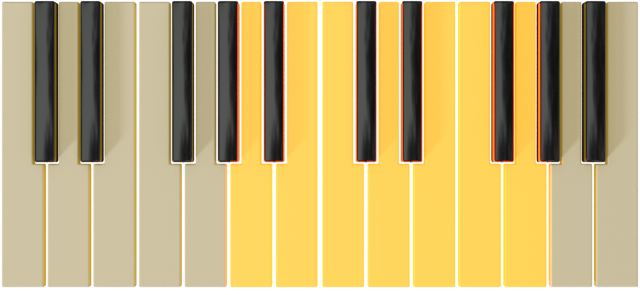 |
 |
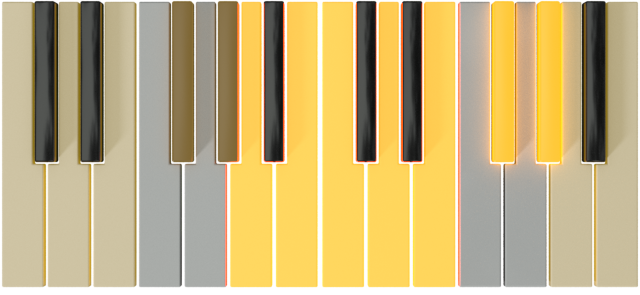 |
| C# |  |
A# |  |
 |
 |
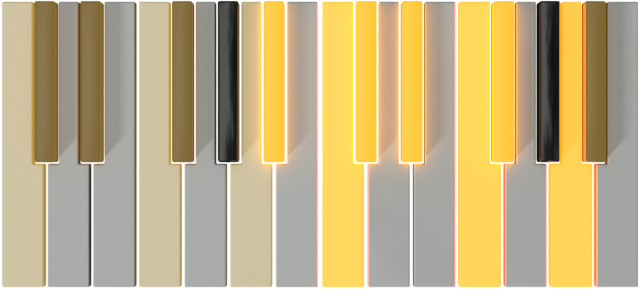
| D |  |
B |  |
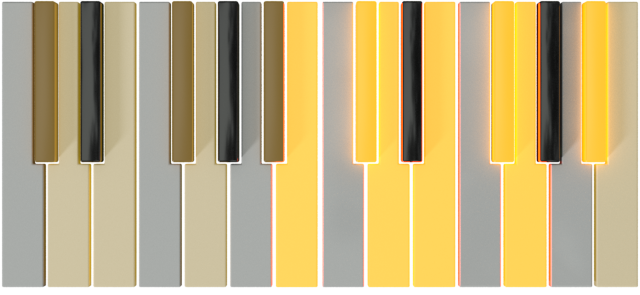 |
 |
| D# |  |
C |  |
 |
 |
| E |  |
C# |  |
 |
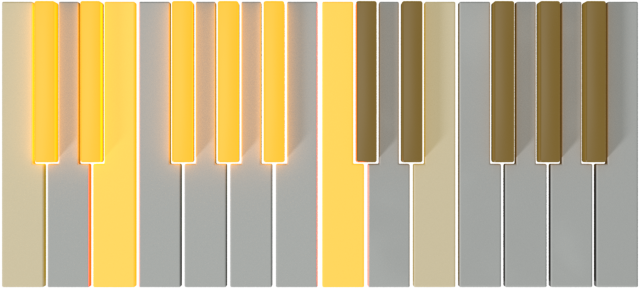 |
| F |  |
D |  |
 |
 |
| F# |  |
D# |  |
 |
 |
| G | 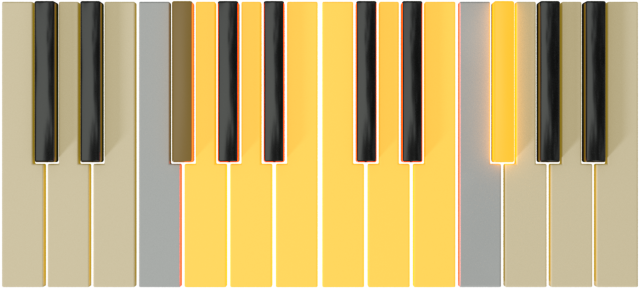 |
E |  |
 |
 |
| G# |  |
F |  |
 |
 |
| A |  |
F# |  |
 |
 |
| A# |  |
G |  |
 |
 |
| B |  |
G# |  |
 |
 |
| Whole (6) | Augumented (6) | Diminish (8) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 1 | 2 1 | |||
 |
 |
 |
https://www.pianoscales.org/chart.html
Mode
mode is scale created by changing tonic mode. to have different flavor. Useful with: complex progression/melody & disregard scale over progression and pick mode for chord
Major modes (relative modes)
| | | | | | | — | — | — | — | — | |C | Ionian | |the major scale |D | Dorian | minor | (Dminor > Gmajor = dorian progression )|natural 6 |E | Phygian | minor | Halfstep at bottom | flat 2 or minor 2nd |F | Lydian | major | Like Ionian or major. | sharp 4 |G | Mixolydian | major | Like Ionina | flat 7 (min7) |A | Aeolian | major || flat 6 (min 6) |B | Locrian | deminished || flat 5
B locr = f lyd // A aeoa = E Phry - same notes dif start ?
when you decide, for whatever reason, to make one particular note your root, that pattern is called the scale, and becomes a ‘parent scale’, as it were, to its other modes: Building a scale with the same key signature but using a different root than the ‘parent’ root becomes a mode: A different fashion/manner of playing the parent scale.
Key
You can play every scale of same key.
- simple chord progression . simple melody
- check scale for all chords in progression
- 15 keys
key signature
Sharpen or flatten for all piece.
https://www.hooktheory.com/cheat-sheet/key/b/locrian
Circle of fifth
Help with: key signature / harmony / intervals / transposition / chord structure …
| Order of sharps | F♯ | C♯ | G | D | A | E | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| number of sharpened notes | 6 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Order of flats | B♭ | E♭ | A♭ | D♭ | G♭ | C♭ | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| number of flattened notes | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 1 |
- Kolejne nuty na kółku są oddalone o (7 semitonów) perfect fifth
- Chords: Common is go only one step . one on left is 4, one on right is 5.
.
| Major | Minor | sharps/flats | order of sharps | order of flats |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | a | - | 2 | 6 |
| G | e | 1♯ | 3 | 5 |
| D | b | 2♯ | 4 | 4 |
| A | f♯ | 3♯ | 5 | 3 |
| E | c♯ | 4# | 6 | 2 |
| B / C♭ | g♯ / a♭ | 7b / 5♯ | 7 | 1 |
| F# / G♭ | d♯ / e♭ | 6♭ / 6♯ | ||
| D♭ C♯ | b♭ / a# | 5♭ / 7♯ | ||
| A♭ | f | 4♭ | ||
| E♭ | c | 3♭ | ||
| B♭ | g | 2♭ | ||
| F | d | 1♭ | 1 | 7 |
Transpose
| steps on circle | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p5 | maj 2 | maj 6 | maj 3 | maj 7 | aug4 | min 2 , 6, 3, 7, p4 |
Harmony
Harmony - chords and progression – porządkuje współbrzmienia dźwięków w utworze,
3 4 5 6 ths - harmony
2nd and 7th dysonant
3, 6 th - most popular harmonized in western
Intervals
Interval are two notes.
- minor 3rd - 2 notes
- Major 3rd - 3 notes between
Chords
3+ notes are creating chord.
Fully extended chord is a scale . CMaj13 is chord that contain
Major Interval + minor Interval = Major cord minor Interval + Major Interval = minor cord (lower middle note )
| Major6 (3-2-1) | Major7 (3-2-2) | Augumented (3-3) | Minor6 (2-3-1) | Minor 7 (2-3-2) | Diminish (2-2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| C# |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| D |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| D# |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| E |  |
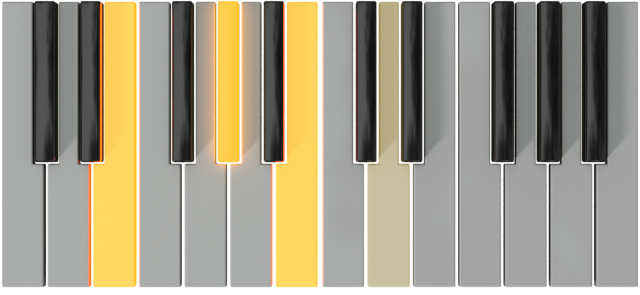 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| F |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| F# |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| G |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| G# |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| A |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| A# |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| B |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Chord Progression
http://www.deniswarren.com/?page_id=3822
2 chord progressions
are well understood, and are the classic cadences, of which V-I (Perfect), I-V (Imperfect), V-VI (Interrupted), IV-I (Plagal) are the most widely used. These are generally used for concluding a phrase.
3 chord progressions
https://youtu.be/RpObAWZ0SKM
I IV V I - common progression
I IV V VI - pop chrods CFG
ii V I - jazz (major and mionor) (bassline: Dmin7 G7 C^) https://youtu.be/cvfN8tG1RwU
IV I vi V -
power cord
1 + fifth (siodmy semitone ) + octave
oscilator
- pierwszy 1 nuta
- drugi + 7 semitones
-----------------------
1 3 5 7 base
(natural) 9 11 13 extension - ALWAYS GROM MAJOR SCALE
-----------------------
C E G B - literraly
B-E-A-D-G-C - 4-ths voiceing (2 odstepu pomiedzy kazydym )
C-G-D + E-B-F# - 5ths voiceing (3 odstepu pomiedzy -)
-----------------------
C maj 7 - (C^)
C, E, G, B
1, maj3, 5, maj 7
C minor 7 (C-7 Cm7)
C, Eb, G, Bb
1, min3, 5, min 7
C dominant 7 (C7)
C, E, G, Bb
1, maj 3, 5, min 7
-------------------------
Intervaal
1 i 8 - daja całą skale odleglosic i te same nuty
interwały
2 3 4 5 6 7 ile półnut po sobie
Tetrachords types:
221 - lydian | major
212 - dorian | minor
122 - phygian | upper minor
131 - harmonic
4
The four-chord cadences, especially those involving I, IV, V and vi are also well-understood
home > predomin > dominant > home
How to find a key you are in:
| Major | I | ii | iii | IV | V | vi | vii’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triads Key | Major | minor | minor | Major | Major | minor | Diminish |
| home tonic | substitution - P.D | substitution D | predominant | dominant | kind of a tonic | ||
| Sevents | Major 7 | minor 7 | minor 7 | Major 7 | Dominnat 7 | minor 7 | Half Dim |
| Minor | i | ii’ | iii | IV | V | vi | vii’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CHORD INVERSION
Music
what is carier and what support
In music sounds of different lengths are used to create rhythmic patterns, and patterns of pitch (in combination with rhythm) become melodic material (whole tunes or shorter ideas). Timbre is the ‘colour’ or tone of the sound: any instrument or voice can produce many different timbres. Dynamics and tempo interact with all these to develop the expressive aspects. Texture and structure are both ways of organising musical ideas, with texture being the
- vertical dimension: one sound or many sounds; rhythmic, timbral and harmonic layering);
-
horizontal dimension: structure being the how musical material is organised in time using repetition, contrast and silence to create the beginning, middle and end of a piece; or cyclical forms
- human can be tuned to listen something “recive rythm, or melody”
Layers
- mixing is important
-
separate to layers
Notation
Clef
𝄞 - G (treble) - FACE (middle c on line one bleow)
𝄡 - C (alto)
𝄢 - F (bass) - ACEG (middle c on line one above)
artykulacja – określa sposób wydobywania dźwięku,
kolorystyka – określa barwę dźwięku.
brzmienie - wydzwiek wszystkiech warstw muzyki poza glowna nutą (gitara fortepian maja inna dynamike i proporcje ) barwy instrumentów
filmowość muzyki - struktura kompozycji by wspolpracowac z napieciami wynikajacymi z obrazu
Tips
- counter melodies
- accent layer (different layers play fragments)
- octaves & passing 5ths in way to higher/ lower octave for base
- 7 K trick (synth hats transient) clear high end - cut synths @ 7 / 7,5K (hats and white noise have room )
- snare should slap
- vocal need to feel clese not far away
https://sonniss.com/gameaudiogdc
audio sources:
- https://www.sound-ideas.com/